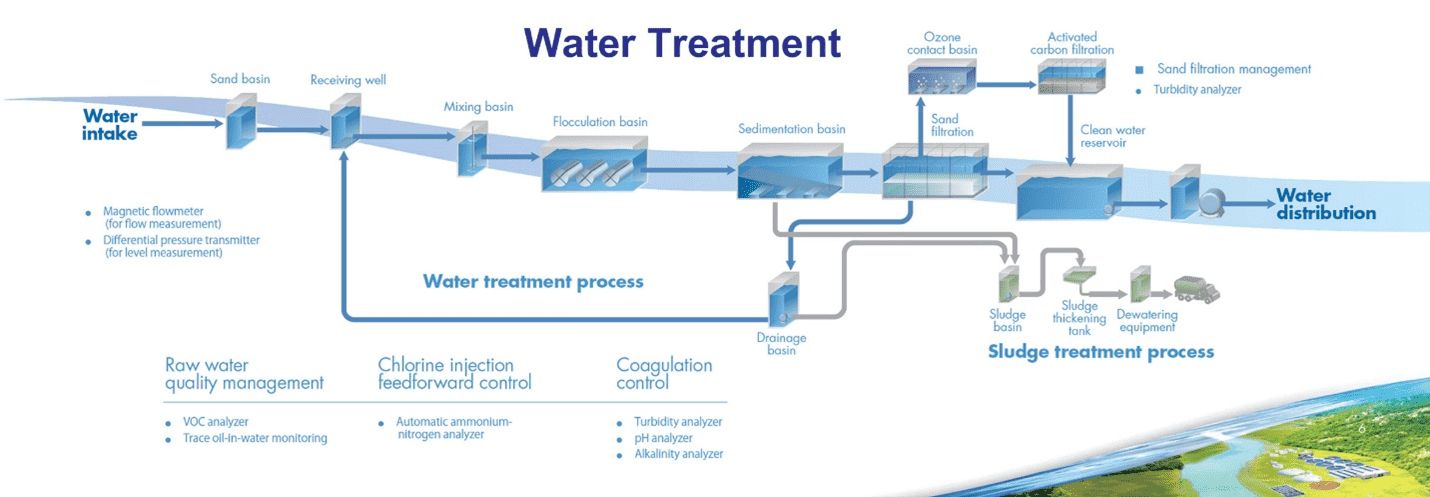
Municipal Driking water treatment and distribution
Smart water automation in municipal drinking water treatment and distribution involves the integration of advanced technologies to optimize the management of water treatment plants and the delivery of safe drinking water to communities. Here are key features and applications of smart water automation being offered by Hydrologic MGP Systems:
1. Real-time Water Quality Monitoring
Deploy sensors throughout the water treatment process to monitor parameters such as turbidity, chlorine levels, pH, and microbial content in real-time.
Implement automated data collection and transmission for continuous monitoring.
2. Automated Water Treatment Processes
Utilize automation to control and optimize various stages of water treatment, including coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection.
Implement advanced control algorithms to adjust treatment parameters based on real-time water quality data.
3. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems
Implement SCADA systems to provide centralized monitoring and control of water treatment plants.
Enable remote access for operators to monitor and control processes from a central location.
4. Smart Metering and Billing
Install smart meters to accurately measure and monitor water usage in the municipality.
Implement automated billing systems for better transparency and control over water expenses.
5. Predictive Analytics for Maintenance
Use predictive analytics to anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance proactively.
Implement condition monitoring systems for critical components to reduce downtime.
6. Water Distribution Network Monitoring
Implement sensors throughout the water distribution network to monitor pressure, flow rates, and detect leaks.
Use automation to identify and isolate sections of the network experiencing issues.
7. Smart Pressure Management
Implement automated pressure control systems to optimize pressure levels in the distribution network.
Reduce energy consumption and minimize leaks through smart pressure management.
8. Automated Reservoir Management
Utilize automation to control water levels in storage reservoirs.
Implement predictive modeling to optimize reservoir levels based on demand and weather patterns.
9. Water Quality Sensors in Distribution Network
Deploy sensors in the distribution network to monitor water quality during transit.
Implement automated flushing programs based on water quality data to maintain water freshness.
10. Remote Alarm and Notification Systems
Implement automated alarm systems to notify operators of critical events or deviations from normal operating conditions.
Enable automated notifications through email or mobile devices for quick response to emergencies.
11. Integration with GIS (Geographic Information System)
Integrate smart water systems with GIS for spatial analysis and mapping of the water distribution network.
Enhance decision-making with location-based information.
12. Data Analytics for Consumer Insights
Use data analytics to analyze consumption patterns and trends.
Implement systems to provide consumers with insights into their water usage for conservation purposes.
13. Compliance Monitoring and Reporting
Ensure compliance with environmental regulations and drinking water standards.
Generate automated reports for regulatory agencies to demonstrate adherence to standards.
14. Public Engagement and Awareness
Implement systems to provide the public with real-time information on water quality and distribution.
Increase awareness of water conservation and promote public trust in the drinking water supply.
Smart water automation in municipal drinking water treatment and distribution enhances overall efficiency, ensures water quality, and promotes sustainable water management practices. It contributes to the delivery of safe and reliable drinking water to communities while optimizing resource usage and minimizing environmental impact.